What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds
You can recognize these compounds because they consist of nonmetals bonded to each other. Amino acids are the molecules.

Tetryonics 59 15 Peptide Bonds Are Formed When The Amine Carboxyl Functional Groups In Amino Acids Interact In A Condensation Reaction And Release Mathematik
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds.
. Covalent compounds also are known as molecular compounds. Amino acids link with each other by mean of peptide bonds covalent chemical bond and form proteins as a result. Starch glycogen cellulose and chitin are examples of polysaccharides.
Covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon-based organic molecules such as our DNA and proteins. Polysaccharides may be very large molecules. Proteins are formed by joining the -CO 2 H end of one amino acid with the -NH 2 end of another to form an amide.
Amino acids are bi-functional compounds containing both a carboxylic acid group -COOH and a basic amino group -NH2 attached to the same carbon atom Fig. Coordinate covalent bonds involve the unequal sharing of an electron pair by two atoms with both electrons originally coming from the same atom. Terms in this set 37 Covalent Bonds.
Dipeptide bonds is the specific name for the covalent bonds. 21 Amino Acid Structure. The measure of an atoms ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond.
Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids exactly the same from one molecule to the next. Covalent bonds are also found in inorganic molecules like H 2 O CO 2 and O 2. For example polypeptides proteins result from the linking of amino acids by peptide bonds and polysaccharides result from the linking of sugars by glycosidic bonds.
Dipeptide bonds is the specific name for the covalent bonds. B A few elements naturally exist as polyatomic molecules which contain more than two atoms. Figure 41 Elements That Exist as Covalent Molecules.
One two or three pairs of electrons may be shared making single double and. The -CONH- bond between amino acids is known as a peptide bond because relatively short polymers of amino acids are known as peptides. The chain may be branched or unbranched and it may contain different types of monosaccharides.
Polymers are molecules that result when similar molecules subunits are linked together by covalent bonds. If the atoms that form a covalent bond are identical as in H 2 Cl 2 and other diatomic molecules then the electrons in the bond must be shared equally. Covalent disulphide bridges SS linking cysteine residues are often involved in the maintenance of tertiary structure.
The primary structure of a protein consists of amino acid residues linked by covalent peptide bonds. Amino acids are the molecules. A protein molecule is made from a long chain of these amino acids each linked to its neighbor through a covalent peptide bond.
The same -CONH- bond forms the backbone of both proteins and synthetic fibers such as Nylon. A long chain of monosaccharides linked by covalent bonds is known as a polysaccharide poly- many. Amino acids themselves are made of atoms joined together by covalent bonds.
A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. Examples of important covalent bonds are peptide amide and disulfide bonds between amino acids and CC CO and CN bonds within amino acids. The primary structure of a protein consists of amino acids chained to each other.
Water soluble positive and negative charges on molecule electrons unequally shared. Cysteine is the sole amino acid whose side chain can form. These are examples of covalent bonds and covalent compounds.
Proteins Amino Acids Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that join amino acids to form polypeptides. The covalent bond that links together two amino acids in a polypeptide Peptide bond Functional units within a larger structure that performs different aspects of a proteins function. Within a protein multiple amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds thereby forming a long chain.
Therefore it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The primary structure of a protein consists of amino acids chained to each other. The electron pair donor is the ligand or Lewis base whereas the acceptor is the.
Most important one carbon atom can join to other carbon atoms through highly stable covalent C-C bonds to form chains and rings and hence generate large and complex molecules with no obvious upper limit to their size see Panel 2-1 pp. Peptide bonds are formed by a biochemical reaction that extracts a water molecule as it joins the amino group of one amino acid. These examples show three molecules found in living organisms that contain carbon atoms bonded in various ways to other carbon atoms and.
For more background on covalent bonds see the covalent bonds page. They are building blocks of proteins. A Several elements naturally exist as diatomic molecules in which two atoms E are joined by one or more covalent bonds to form a molecule with the general formula E2.
They are linked together by a peptide bond see later. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1. Electrons shared in pure covalent bonds have an equal probability of being near each nucleus.
Organic compounds such as carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids are all examples of molecular compounds. What molecules form protiens when linked together with covalent bonds. Proteins are therefore also known as polypeptides.
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. Amino acids are organic molecules that contain amino group and carboxyl group. A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
In addition to the covalent bonds that connect the atoms of a single amino acid and the covalent peptide bond that links amino acids in a protein chain covalent bonds between cysteine side chains can be important determinants of protein structure. We refer to this as a pure covalent bond. Peptide Bonds.
Strongest chemical bond between two atoms two atoms share electrons. What molecules form protiens when linked together with covalent bonds.
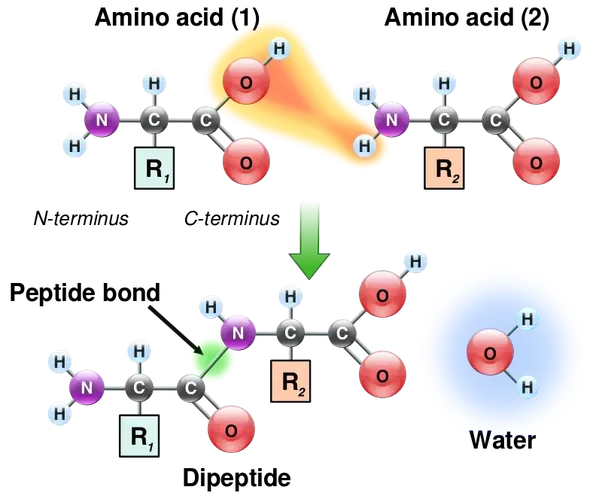
What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds Socratic

Protein Structure And Its Function Britannica
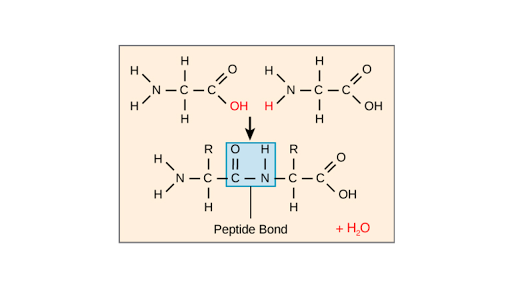
Introduction To Proteins And Amino Acids Article Khan Academy

Bonds Used In Protein Structure Biology Exams 4 U Protein Biology Biology Lessons Peptide Bond
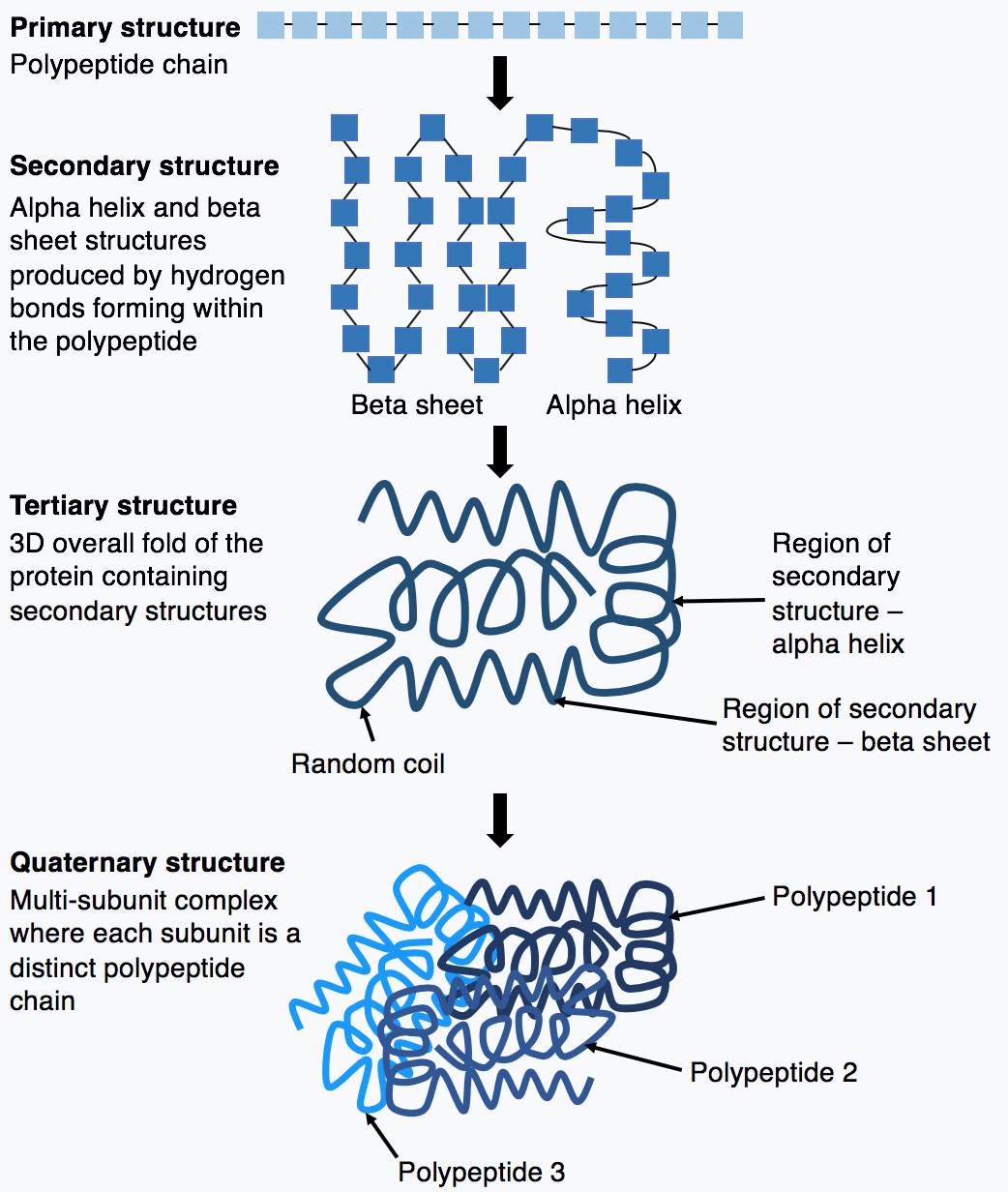
Protein Structure Amino Acids Primary Teachmephysiology

Click The Link In Our Bio To Find Demo Tutorials Quiz Questions And An Interactive Drawing Pad With Starter Images A Covalent Bonding Biochemistry Med Student
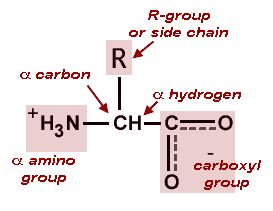
What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds Socratic

Tetryonics 109 05 Disulfide Bridges Are Created Between Any Two Closely Spaced Cysteine Peptide Molecules In Complex Polypeptide Chains In Turn Facilitating P
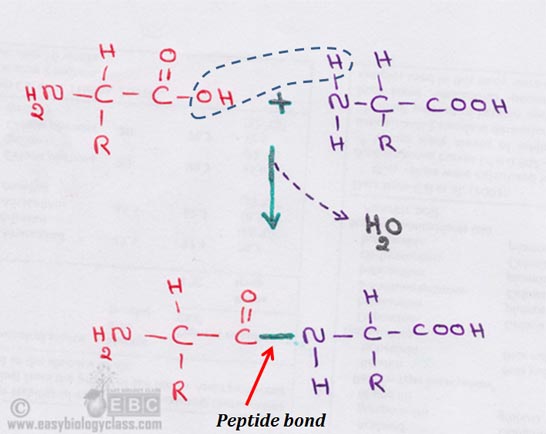
Chemical Bonds In Protein Biochemistry Notes Easy Biology Class

Protein Structure A Level Notes
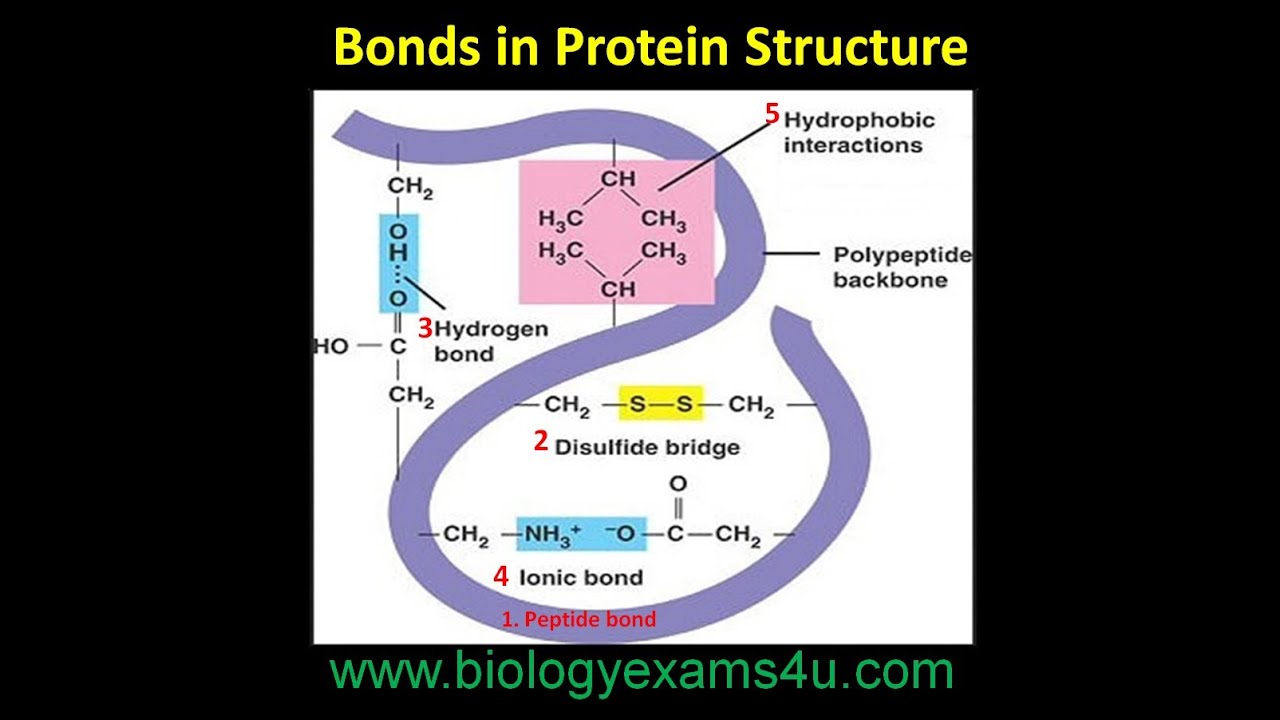
Bonds In Protein Structure Youtube
Chemical Bonds In Protein Biochemistry Notes Easy Biology Class
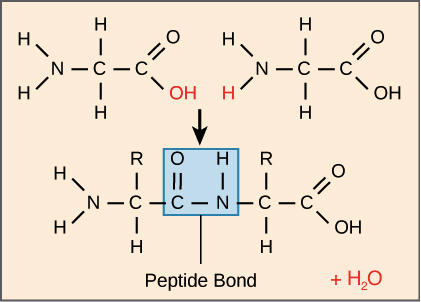
Introduction To Proteins And Amino Acids Article Khan Academy

Learn About The 4 Different Types Of Protein Structure Protein Biology Biochemistry Teaching Biology




Comments
Post a Comment